Why even think about data-types?
Let us take a look at data-types. Beginners are often confused when they encounter some unconventional data-types being used in embedded c programming. What we must realize is that, the resources on an embedded system are often limited, even declaration of the sub-optimal data-type will lead to wastage of memory.
So, what should be done?
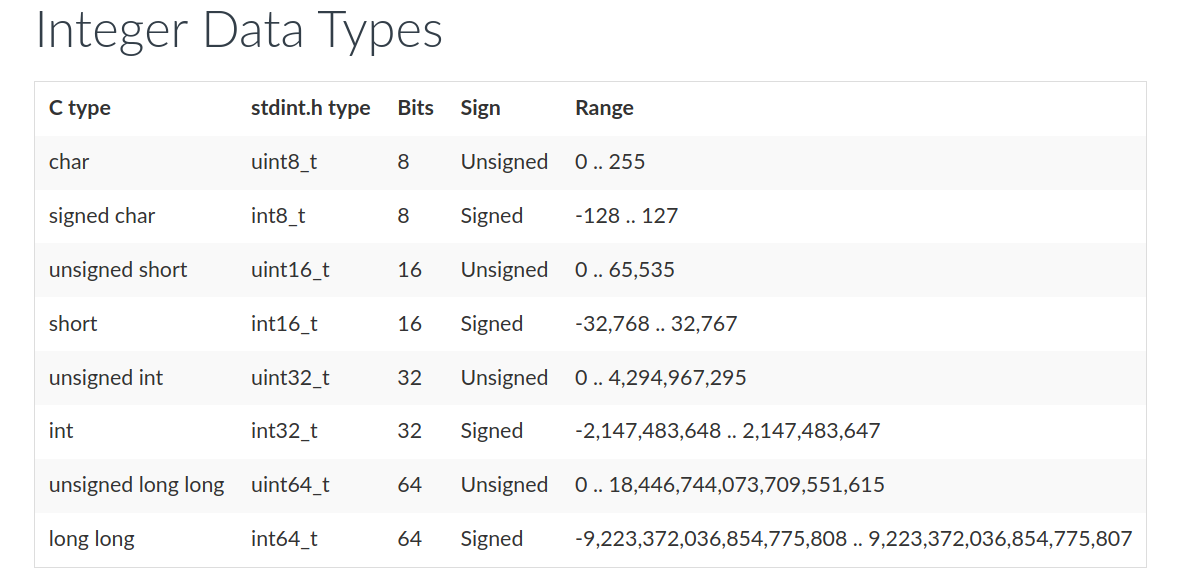
The question is what is the optimal data-type? As we can see from the table attached below, unsigned char and signed char are 8-bit in size. And for our purposes, AtMega328 is an 8-bit microcontroller, which means that it can fetch 8 bit data from memory, the data-bus is 8-bit and the registers in RAM for temporary storage also have to be 8-bit in size.
Unsigned/Signed Char: Thus, Unsigned/signed char is the most widely used data-type in AVR programming. Further optimization can also be brought about by thinking of whether to use signed or unsigned char, based on the range(and sign) of values that you are going to deal with.
Unsigned/Signed Int: Int will take up 16-bit size in the memory, which will take up 2-bytes of RAM.
Float and Double: These are used to deal with fractional numbers. Double has higher precision than float. Both are 32 bit in size.
Unsigned/Signed long: It is used when 16-bit int or 32-bit double will not suffice, again appending long will lead to increase in hex file size.
And that is it! But wait… there’s more:
An alternative that programmers use, and one which you will come across most of the time in embedded programs is, uint8_t. In general one can use these “uint< bit size >_t”, which are equivalent to typedef of the previously known data-types.
Namely - uint8_t, uint16_t, uint32_t and uint64_t correspond to unsigned char, unsigned short, unsigned int and unsigned long long, respectively. Same goes for their signed counter-parts.
Note that unint8_t (and similar family of declaration) is the one which you will be using most of the time as this will give you a clear indication and control over the bits. Also, just for reference, uint< bit size >_t family is under stdint.h header file.
Reference table for different data-types in C -
Author - amm0
Check out the book by Mazidi - AVR Microcontroller embedded programming, for more info. Also the bread and butter of every firmware engineer, AtMega328 datasheet. If you have questions or suggestions, you can reach out to me via email or on facebook.